Impulse Oscillation
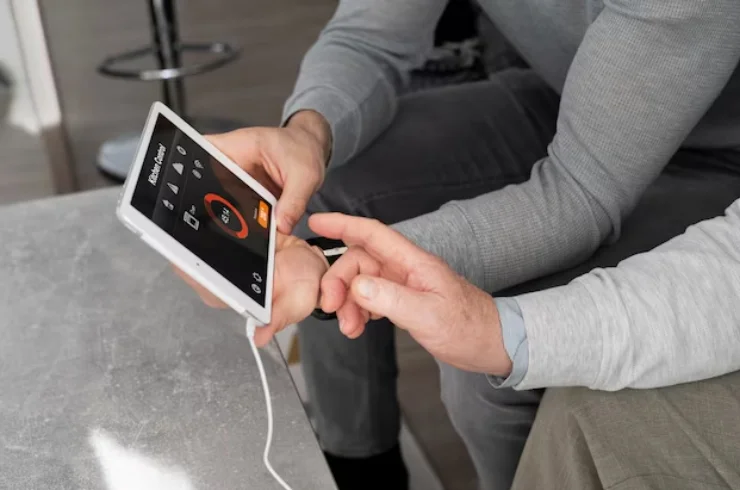

Impulse Oscillometry (IOS) is a non-invasive test used to assess lung function, specifically the mechanical properties of the airways. It is part of pulmonary function testing (PFTs) and is particularly useful for diagnosing and monitoring conditions like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and other respiratory diseases.
How Impulse Oscillometry Works:
During the test, the patient breathes through a mouthpiece while a small, painless oscillating pressure signal is applied to the airways. The device measures how the lungs respond to this oscillation, recording the resistance and reactance of the airways at different frequencies.
- Resistance (R): This refers to the opposition to airflow in the lungs. It can indicate how narrow or obstructed the airways are.
- Reactance (X): This refers to the elastic properties of the lung tissue and airways, reflecting how the lung tissue and airway walls are able to stretch and recoil.
Applications of Impulse Oscillometry:
- Early detection of airway diseases: It can detect subtle changes in lung function before symptoms are noticeable.
- Monitoring disease progression: IOS can help track changes in lung function over time, especially in conditions like asthma or COPD.
- Assessment of treatment response: It is useful for evaluating the effectiveness of medications, such as bronchodilators, in improving airflow.
Impulse oscillometry is a valuable tool for providing a detailed view of lung function, especially for patients who may find other tests, like spirometry, difficult to perform a